|
Welcome
In this tutorial we will help you complete the task of importing or processing data from multiple worksheets from one Microsoft Excel workbook file.
We will demonstrate how to configure a task to complete this goal, and be able to quickly repeat the process time and time again.
 |
If you need help with this task, drop us an email to Support@LeanSoftware.net, with an example spreadsheet, we may well be able to help you. |
In this first example we show you how to import or update existing data in a table, later we will create how-to examples to show you how to send the data to a stored procedure.
Setting up the task is a do it once process - EDT saves all your task settings into a task XML file. The next time you want to repeat the process you simply select the Task from the main EDT interface.
|
Be aware before we start - What are the pitfalls of importing Excel data into SQL Server?
Often companies experience intermittent data import failures when trying to import Excel data.
Your database administrator will be quick to tell you there are going to be problems if you plan to do this regularly.
So how can we make this a secure and reliable process? How can the EDT software help you?
Validation, validation, validation..
- With a visual interface that allows you to correct the data
- Automatic validation highlighting any problems on a per-row basis.
- Validation is not just data type validation - but validation with the destination database itself - this being wrapped in a transaction that is always undone on any validation problem.
- Any number of validation rules can be added.
- Data can be sent to a stored procedure for more advanced validation, the procedure can return validation error messages.
How does EDT compare to other import techniques?
Compared to any other import method EDT gives a huge advantage, and provides a highly reliable import method.
The reason companies have problems importing Excel data is the fact that users can modify data formats or make other changes that render the data or file invalid. EDT efficiently overcomes all these Excel import problems improving business efficiency and data accuracy.
Worked example - Import from Multiple Excel worksheets to SQL Server Table
Here we assume you have already downloaded the EDT software (you can run this example even with the trial version, please see download page).
We will see how EDT can help you to easily :
- highlight and reject rows with missing essential data
- combine data from two worksheets
- validate data against fixed list or sql lookup list
In this example we will load, modify, validate and upload data from these two sample worksheets.
Example source data Sheet1

Example source data Sheet2

STEP 1 - Create New Task
Click the New task option to create a new EDT Task.

Enter a task name, select the insert or update table from any source option.

Click Next and you will be brought to the target connection configuration page. Click new to connect to a target.

STEP 2 - Connecting to SQL Server
In this example we will use one of the Native SQL Server drivers:

Enter the essential connection details only :
- Name of your SQL Server
- Connection method (either Windows NT Intergrated security or a specific user name and password)
- Select Database name
- Test the connection

STEP 3 - Select destination table

- NOTE : The chosen destination partly determines the layout of columns in the task
- EDT can thought of as 'using Excel as a Workspace', the layout of the workspace is determined by the data Destination,
- the data displayed (from the data source) is overlayed on top of the destination layout and is determined on the 'Data source / SQL' configuration tab.
- A task does not have to have data source, data can be pasted into a task from the clipboard if you wish, but generally it is much better to use the data source tab as data can be imported from any source.
- Using the 'Destination columns / SQL tab screen' as shown above you can:
- Define task column layout using drag and drop of the column name
- Hide unwanted columns
- Exclude unwanted columns from the SQL
- Insert what we call 'Work columns' - a user defined column that can be used for several purposes - a calculated value for example.
- Apply validation and formatting rules can be applied (data type validation is automatic)
- Define display formatting for example dates and money amounts
- Create 'SQL lookup' columns that can retrieve existing values from the database that match the imported data
- And more!
We will stick to the basics for the purpose of this tutorial.
|
STEP 4 Create the ODBC data source
 |
Using ODBC is just one way of connecting to Excel spreadsheet data. You can use alternative connection methods, and you can paste a connection string into the connection string text box. Please see the EDT reference section Excel Data Source Connection Strings |
To connect using ODBC, click the 'Data source / SQL' tab. Click ODBC 32 to create a new ODBC connection to launch the windows ODBC administrator:

Click Add in the ODBC administrator:

Select the correct Excel ODBC Driver : In this example we are going to use the 'Microsoft Excel Diver (*.xls)

Provide a Data source name and select the XLS workbook using the dialogue, select OK to close the ODBC administrator and return to EDT.

STEP 5 - Select the ODBC data source
Click the New button

Select provider Microsoft OLE DB Provider for ODBC Drivers, click Next..

Select the ODBC Excel data source that you created, click Test
Click OK to return to EDT:

|
As shown in the above screenshot you will now see now how easy and brilliantly flexible it is to select data from the Spreadsheet Worksheets using EDT !
- You can select a specific worksheet using the Object Source dropdown
- In our example we will start with using Sheet 1 then we will modify the SQL to combine data from Sheet1 and Sheet2
- SQL is generated for you and by default all columns are included
- If you click the 'Custom' SQL radial option - you can manually edit the SQL as you require
- You could modify the SQL to only select a sub set of the data for example by adding a WHERE clause
- The SQL can be modified to only select certain columns form the worksheet
- Add blank columns if you wish by using the NULL keyword eg SELECT [WebCustomerID], NULL, [Email]..
- Click the 'Test' button to check the SQL syntax and view the first 100 records
- You can click the Map Columns button to reorder the select list using drag and drop - showing you a mapping between the destination and source columns
- You can insert Task Parameters using the parameter insert button
 this allows you to load data matching user parameters - such as a category or date range (User parameters are created using the Parameters tab) this allows you to load data matching user parameters - such as a category or date range (User parameters are created using the Parameters tab)
|
STEP 5 - Column Mapping
Click the Map Columns button


In the example shown above we have initially aligned the columns that match exactly, these being highlighted in red.
You can drag and drop to alter the position/order of both the source and destination columns.
We now need to exclude the unwanted columns, this will complete in step 8 and 9.
Notice the source has a First name and Last name, but the destination only has a Name field, this we will deal with in Step 10.
STEP 6 - Excluding unwanted Source columns
Click the custom SQL option and remove the unwanted source columns from the SQL:

Click Test SQL to verify the syntax and view the data that will be returned by the query:

STEP 7 - Excluding unwanted Destination columns
On the Destination tab for unwanted columns,
- uncheck the Mandatory option,
- uncheck the Include in SQL option
- uncheck the Visible option

Notice that the SQL on the right hand panel is automatically updated to include only the columns required.
STEP 8 - Custom SQL to concatenate First and Last name fields
To concatenate the first and last name into one column we simply modify the Source SQL to append two fields using the ampersand operator , separating with a space:

STEP 9 - Test the Task
Save the task and return to the main EDT interface, and we will see the data loaded and ready to be imported.

STEP 10 - Remove unwanted rows
Often a spreadsheet will contain unwanted rows, these might be blank rows or rows that contain total/sum amounts.
As you can see in the above screenshot our data contains some blank rows at the end, these we will remove using the very useful SQL function ISNUMERIC() field to check for a value in column in the spreadsheet.

STEP 11 - Add data validation rules
|
There are several ways that EDT handles data validation within your task - ensuring the data is of good quality and good news for your business!
- Data type validation (automatic)
- Mandatory / must have values
- Add one or more specific validation rules by column using the power of Excel Data validation
- Validation by batch - specifying that all rows rows must be valid before the Send button operation is used
- Validation using fixed lists or SQL lookup Lists
- Server validation - automatic by use of the Validation button
- Additional server validation - applicable when sending data to a stored procedure
|
In this example we will add three validation rules:
- Email address must be supplied
- Name bust be more than two characters long
- Country must match one of our existing entries the County table, and the allow the user to correct the data by selecting from a drop down list
Marking an item as Mandatory
This is very easy - just click the Mandatory checkbox next to the data item name:

When the data is loaded into the task, any missing mandatory data is highlighted.
Notice that the Active Legend Red status shows a count of two rows . You can use the legend up/down arrows to very quickly locate the rows in each status band.
The left hand column shows the user what is wrong, and the problem cell has a red border:-

Using the power of Excel Data Validation!
Here we will add a validation rule specifying the Name value must be more than two characters.
Click the Excel validation button:

Additionally, on the Error Alert tab, enter an error description for user feedback:

Notice that multiple validation messages appear when on row 16 of this example, as two column values are invalid:
Validation with Lists
In our example we are importing a Country value, but it must match with a valid country name in an existing Country table in SQL server database.
We can easily use the EDT sql lookup column capability to validate these values.
Click the SQL list button on the Country row item :

Choose options as shown below to create a Lookup column:
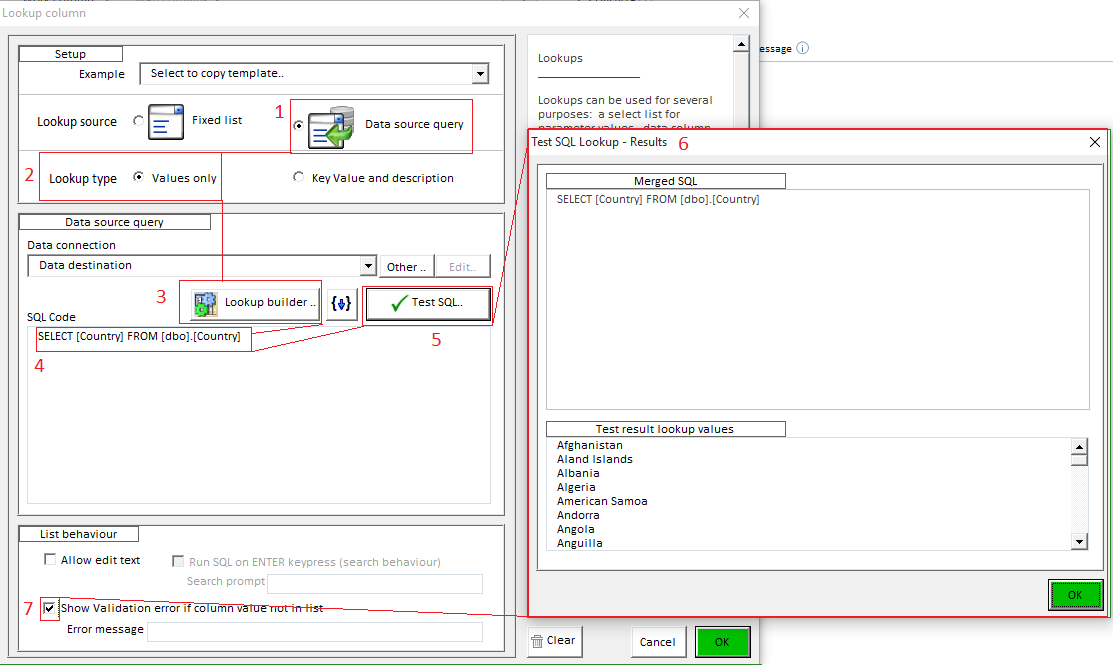
The option shown at the bottom of the dialogue Show validation error if column value not in list must be ticked for lookup validation to take place.
Returning to EDT as you can see below, it is now obvious there are some spelling errors in the country name data:

The user can simply click on the country cell and select the correct country name from the drop down list!

STEP 12 - Combine data from a second Worksheet
We can think of each worksheet as a
table in SQL terms.
All we need to do, to include rows from multiple worksheets is to UNION the worksheet rows together.
In this example, the two sheets have the same column names, and the order of the columns is the same.
Of course they may not be in your scenario, but it is just a case of constructing the correct SQL to combine data from as many worksheets as you need.